By : TZX UAV
Click : 5210
Agricultural drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for agricultural use, have emerged as a key technology driving the modernization of agriculture. These drones are equipped with advanced sensors, GPS navigation systems, and automated control systems, enabling them to perform a variety of tasks in agriculture with precision and efficiency.

Key Transformations in Modern Agriculture
Efficient Pest Control and Fertilization
Agricultural drones can be used for precise pesticide application and fertilization. By using drones, farmers can target specific areas of their fields that require treatment, reducing the amount of chemicals used and minimizing environmental impact.
Drones can also cover large areas quickly, ensuring timely and uniform application of pesticides and fertilizers, which leads to healthier crops and increased yields.
Crop Monitoring and Data Collection
Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, agricultural drones can capture detailed images and data about crop health, soil moisture, and other critical factors.
This data can be analyzed to provide farmers with insights into the best practices for their fields, such as optimal irrigation schedules and nutrient application rates.
Seeding and Planting
Drones are also being used for precision seeding and planting. By using drones, farmers can ensure that seeds are planted at the optimal depth and spacing, leading to more uniform and healthy crop growth.
Cost Savings and Labor Reduction
The use of agricultural drones reduces the need for manual labor in many agricultural tasks. This not only saves costs but also reduces the physical strain on farmers.
Additionally, drones can operate in difficult-to-access areas, such as hillsides or wetlands, making them more versatile than traditional agricultural machinery.
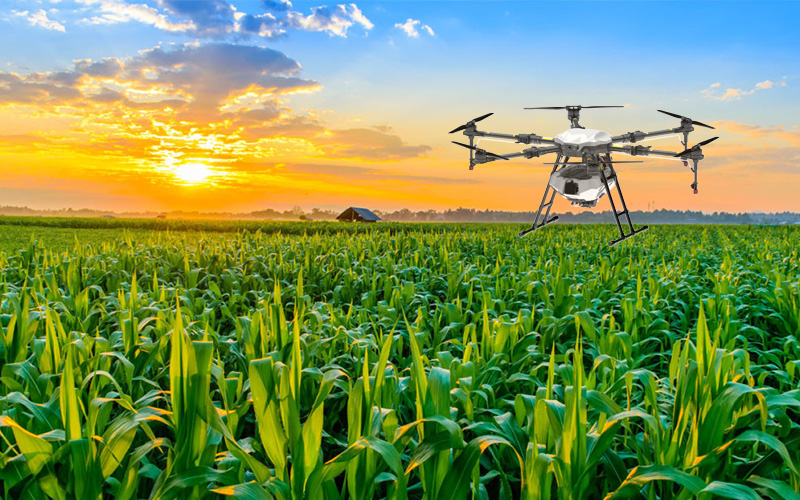

Examples of Agricultural Drone Applications
Large-Scale Operations
Companies like TZX agricultural Drones have developed large-scale drone systems capable of performing agricultural tasks over vast areas. Their drones, such as the NV series plant protection drones, have been used for pesticide application, fertilization, and crop monitoring.
Commercial Use Cases
DJI, a leading drone manufacturer, has also ventured into the agricultural sector with its range of agricultural drones. These drones are capable of precision application of pesticides and fertilizers, as well as crop monitoring. DJI's drones have been used in over 100 countries and regions, with a cumulative operation area exceeding 75 billion mu (a traditional Chinese unit of area, approximately equal to 0.0667 hectares).
Challenges and Future Prospects
Technical Challenges
While agricultural drones offer many benefits, they also face technical challenges such as battery life, payload capacity, and navigation accuracy.
Research and development are ongoing to overcome these challenges and improve the performance of agricultural drones.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment for agricultural drones is constantly evolving. Governments are working to establish clear guidelines and regulations to ensure the safe and effective use of these drones.
As the technology matures and regulations become more streamlined, it is expected that the adoption of agricultural drones will accelerate.
Future Prospects
The future of agricultural drones is bright. With ongoing research and development, these drones are expected to become more sophisticated and capable of performing a wider range of tasks.
Additionally, as the cost of drones continues to decrease and their performance improves, it is likely that they will become more accessible to small-scale farmers, further democratizing precision agriculture.
Agricultural drones are transforming modern agriculture practices by providing efficient, precise, and cost-effective solutions for pest control, fertilization, crop monitoring, and other critical tasks. As technology continues to advance and regulations become more streamlined, the adoption of these drones is expected to accelerate, further democratizing precision agriculture and improving the productivity and sustainability of agricultural systems worldwide.